dbt の Getting Started で初めて触ったときのメモ
dbt (Data Build Tool) とは
ELT, ETL の “T” の部分を効率化する、データエンジニア向けの SaaS ですね。 主に言われている特徴はこんなところかな。気に入ったところ書き足したら多くなってしまった
- warehouse ごとの DDL よりも抽象化された「モデル」定義を SQL の select 文 や Python DataFrame で書けばよく、 warehouse ごとの書き分けが不要。 view or table とかも都度書く必要がない
- モデル定義はモジュール化して再利用可能
- macro, hook, package management の恩恵を受けて DRY に作れる
- クエリにかかる時間を削減してくれる (メタデータを駆使してええ感じにするらしいけどわかってない)
- GitHubなど使ったソースコード管理でブランチングやバージョン管理に対応
- データクオリティを保証するために test を書ける
- ドキュメントの自動生成、リネージュによる可視化
チュートリアルやってみる
https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/get-started/getting-started/building-your-first-project に沿ってあれこれやってみるぞい。
connect dbt Cloud to BigQuery
dbt側にコネクタが用意されているので簡単。 BQ 側で必要な Credential を json で生成したらそれを dbt Cloud に食わせたら Test Connection に成功。という感じ。
Reposigoty
dbt Cloud マネージドなリポジトリがあるので、 quickstart ではそこを使う。 でもちゃんとやるなら GitHub, GitLab, Azure DevOps などをおすすめするとのこと。そうだね。
model 作成
テーブルやビューの定義をするもので、1個の sql ファイルに対応するイメージを得た。 DDL 書いた .sql ファイルでもう model ともいえるが、 dbt では model 間の依存関係とかを定義できるのが一味違う。
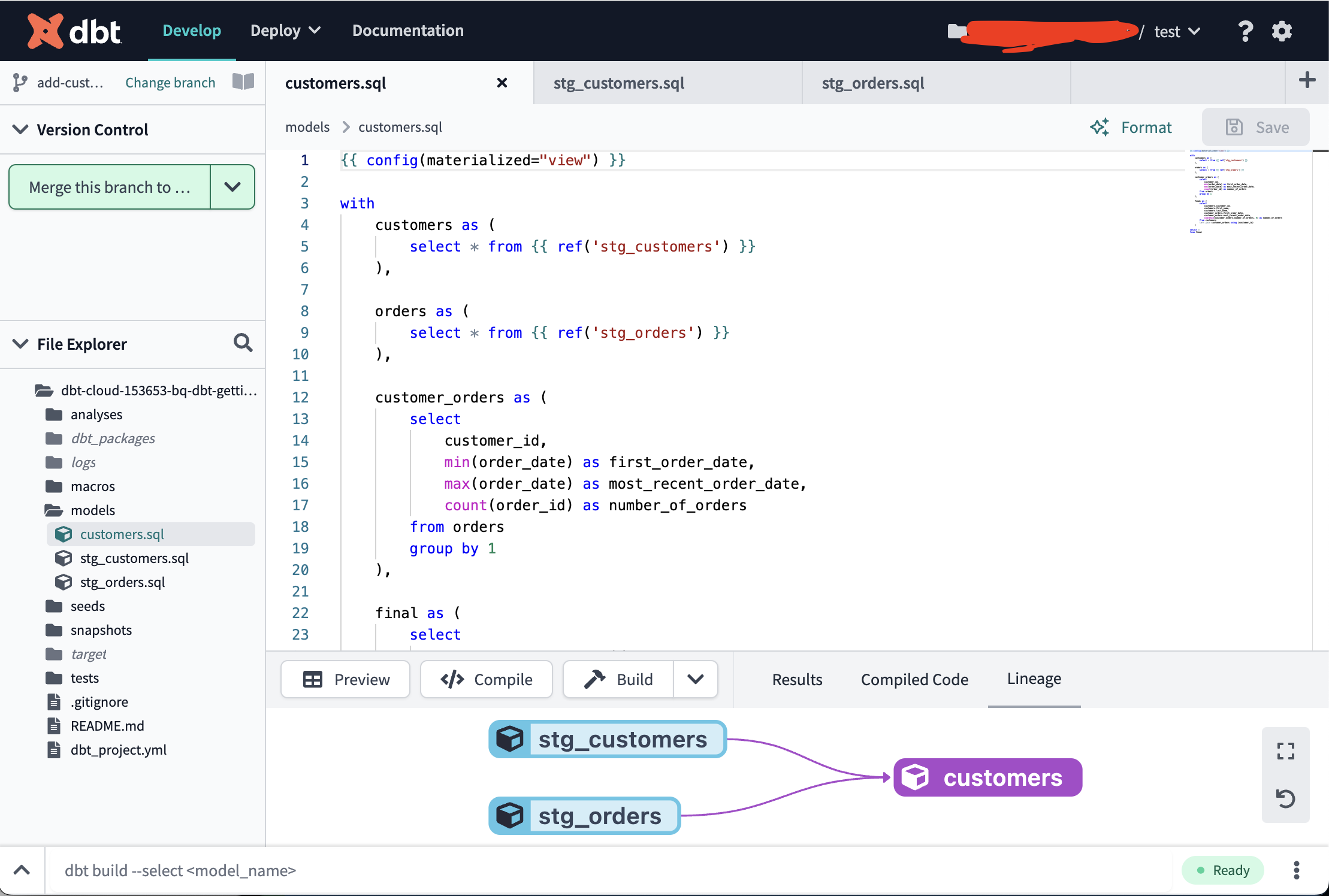
簡単なモデル定義の例を models/stg_customers.sql で紹介:
select
id as customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
from `dbt-tutorial`.jaffle_shop.customers
select 文を書くだけで、 create table は不要。
実はこれでテーブルを作るのかビューを作るのかは、別のところで設定する。
それが dbt_project.yml で、この例だと最後の3行 models 配下:
name: 'jaffle_shop'
version: '1.0.0'
config-version: 2
profile: 'default'
model-paths: ["models"]
analysis-paths: ["analyses"]
test-paths: ["tests"]
seed-paths: ["seeds"]
macro-paths: ["macros"]
snapshot-paths: ["snapshots"]
target-path: "target"
clean-targets:
- "target"
- "dbt_packages"
models:
jaffle_shop:
+materialized: table # jaffle_shop のモデルをマテリアライズするときにはテーブルを作る、と宣言している
さらに2個。 ref を使って他のモデル定義を参照することもできるし、
materialization などの設定を個別に上書きすることも可能というのを models/customers.sql で紹介:
{{ config(materialized="view") }} -- 設定の上書き
with
customers as (
select * from {{ ref('stg_customers') }} -- 別のモデル定義の参照をすることで、 stg_customers テーブルを参照する SQL 文にコンパイルされる
),
orders as (
select * from {{ ref('stg_orders') }}
),
customer_orders as (
select
customer_id,
min(order_date) as first_order_date,
max(order_date) as most_recent_order_date,
count(order_id) as number_of_orders
from orders
group by 1
),
final as (
select
customers.customer_id,
customers.first_name,
customers.last_name,
customer_orders.first_order_date,
customer_orders.most_recent_order_date,
coalesce(customer_orders.number_of_orders, 0) as number_of_orders
from customers
left join customer_orders using (customer_id)
)
select *
from final
ちなみに model 定義を作って dbt run すると
接続先の warehouse (BigQuery, Databricks, Snowflake, Redshift, PostgreSQL, etc.) にテーブルやビューが作成されるが、
model を削除したからと言ってそれらが消えることはないらしい。手動で削除せい、とのこと。安全のためかな。
Tests と Documentation
テストもドキュメントに必要な情報も、 models/schema.yml に yaml で記載する感じ。
version: 2
models:
- name: customers
description: One record per customer
columns:
- name: customer_id
description: Primary key
tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: first_order_date
description: NULL when a customer has not yet placed an order.
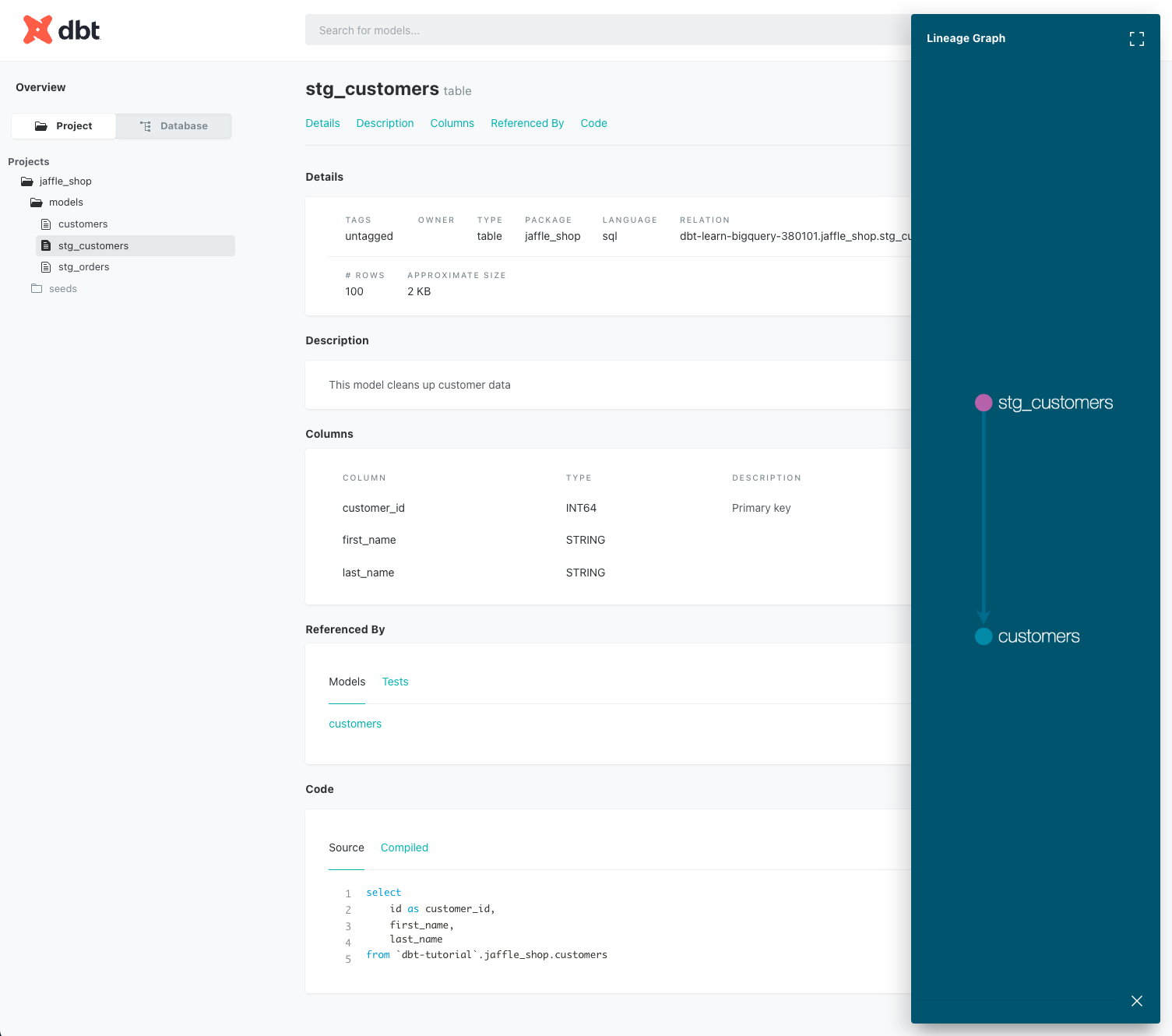
- name: stg_customers
description: This model cleans up customer data
columns:
- name: customer_id
description: Primary key
tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: stg_orders
description: This model cleans up order data
columns:
- name: order_id
description: Primary key
tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: status
tests:
- accepted_values:
values: ['placed', 'shipped', 'completed', 'return_pending', 'returned']
- name: customer_id
tests:
- not_null
- relationships:
to: ref('stg_customers')
field: customer_id
description が documentation での説明のためだけのもの。 tests 配下に not_null などのテスト要件を書いている。
test の実体
not_nullの実体はこんな感じで、 null のレコードをカウントしてエラー判定している。-- テスト結果判定のための定形部分 select count(*) as failures, count(*) != 0 as should_warn, count(*) != 0 as should_error from ( -- テスト内容によって変わる部分 select customer_id from `dbt-learn-bigquery-380101`.`jaffle_shop`.`customers` where customer_id is null ) dbt_internal_test
Documentation
説明と Lineage を自動生成してくれる。 まあまあほどほどのものかなって感じがする。
Environment
Dataset (RDBMSでいうスキーマの部分に相当) をここで切り替えていた。 もっと色々できないのかな…?
Jobs
ここでは「dbt seed, run, そのあとに test する」などの決められたプロセスを定義して何度も実行できる形で管理してくれる。 定期スケジュールしたり、 CI でキックされたり。
Seed
静的に作りたいテーブルとそのデータを定義するための機能で、
dbt seed を実行して seeds/tablename.csv の中身をデータとして生成される。
seed で作るテーブルは model では定義しない。やると2重定義みたいになってエラーで怒られる。
確認したいこと
- モデル定義の sql 文では、 warehouse ごとの方言とかはどう吸収されるんだろう…?
- macro で楽することがあるようで、 macro の中身は warehouse ごとの場合分けも発生し得るそう。
- Environment: もっと他のパラメータも指定できないのかな?
- なさそう